Mitosis vs meiosis worksheet answers – Mitosis vs. Meiosis Worksheet Answers: Dive into the captivating world of cell division, where the intricate processes of mitosis and meiosis unfold, shaping life’s very foundation. This comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of these fundamental biological phenomena, providing a thorough understanding of their significance in growth, reproduction, and genetic diversity.
Throughout this exploration, we will delve into the distinct stages of mitosis and meiosis, examining the meticulous choreography of chromosomes and spindle fibers. We will uncover the profound implications of these processes, from tissue repair to the creation of genetic variation, unraveling the intricate tapestry of life’s cellular machinery.
Mitosis vs. Meiosis Comparison
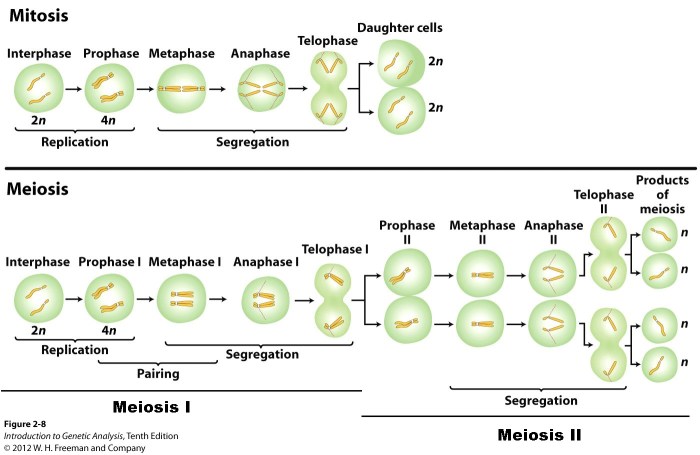
Mitosis and meiosis are two distinct types of cell division that serve different purposes in the life cycle of eukaryotic organisms. Mitosis is responsible for the growth and repair of tissues, while meiosis is involved in the production of gametes (sex cells).
The following table summarizes the key differences between mitosis and meiosis:
| Process | Number of Daughter Cells | Number of Divisions | Purpose | Chromosome Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitosis | 2 | 1 | Growth and repair of tissues | Diploid (2n) |
| Meiosis | 4 | 2 | Production of gametes | Haploid (n) |
Mitosis Process
Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells. It is a continuous process, but for the sake of study, it is divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.During prophase, the chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope begins to break down.
The spindle fibers, which are responsible for separating the chromosomes, begin to form. In metaphase, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. The spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes and begin to pull them apart. In anaphase, the chromosomes continue to be pulled apart until they reach opposite ends of the cell.
In telophase, two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the spindle fibers disappear.The role of chromosomes and spindle fibers in mitosis is essential. Chromosomes carry the genetic material of the cell, and spindle fibers are responsible for separating the chromosomes so that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
Meiosis Process
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, creating haploid cells. It occurs in two stages, meiosis I and meiosis II, each consisting of four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Stages of Meiosis I
- Prophase I:Chromosomes condense and become visible. Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. This results in genetic diversity among the daughter cells.
- Metaphase I:Homologous chromosome pairs line up at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase I:Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I:Two daughter cells are formed, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Stages of Meiosis II, Mitosis vs meiosis worksheet answers
- Prophase II:Chromosomes condense again and the spindle apparatus forms.
- Metaphase II:Chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase II:Sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase II:Four haploid daughter cells are formed, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Formation of Haploid Cells and Genetic Diversity
Meiosis produces haploid cells, which contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This is essential for sexual reproduction, as the fusion of two haploid gametes (e.g., sperm and egg) restores the diploid chromosome number in the zygote.
Crossing over during prophase I leads to genetic diversity among the daughter cells. This is because the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes creates new combinations of alleles. As a result, the offspring of sexually reproducing organisms exhibit a wider range of genetic variation than asexually reproducing organisms.
Practice Problems: Mitosis Vs Meiosis Worksheet Answers
To reinforce understanding of mitosis and meiosis, students can engage in practice problems designed to assess their grasp of the processes, stages, and genetic outcomes.
Stage Identification
Students can identify specific stages of mitosis and meiosis based on provided images or descriptions. This helps them visualize and differentiate between the key events occurring in each stage.
Process Comparison
Students can compare the processes of mitosis and meiosis by completing tables or diagrams that highlight the similarities and differences. This fosters their understanding of the unique characteristics of each process.
Genetic Outcome Analysis
Students can analyze the genetic outcomes of mitosis and meiosis. For instance, they can predict the number of daughter cells produced, the ploidy of the cells, and the genetic variation introduced during meiosis.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the primary difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse daughter cells.
How many divisions occur during mitosis?
One division
What is the role of crossing over in meiosis?
Crossing over shuffles genetic material between homologous chromosomes, creating genetic diversity.