The Giger Davidhizar Transcultural Assessment Model (GD TAM) is a widely recognized framework for assessing cultural diversity and its impact on healthcare interactions. Developed by Marilyn Anne Giger and Joyceen Boyle Davidhizar, this model provides a comprehensive approach to understanding cultural influences on health beliefs, values, and behaviors, empowering healthcare professionals to deliver culturally sensitive and equitable care.
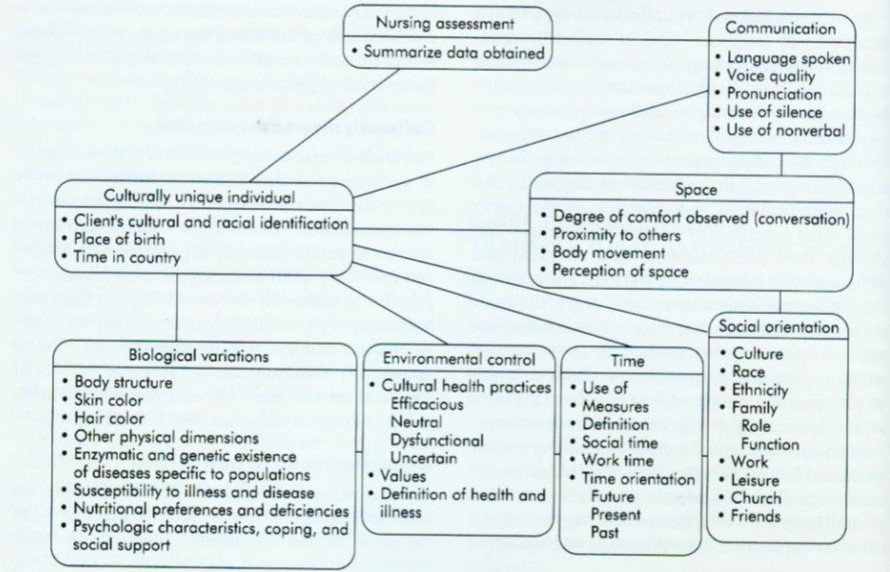
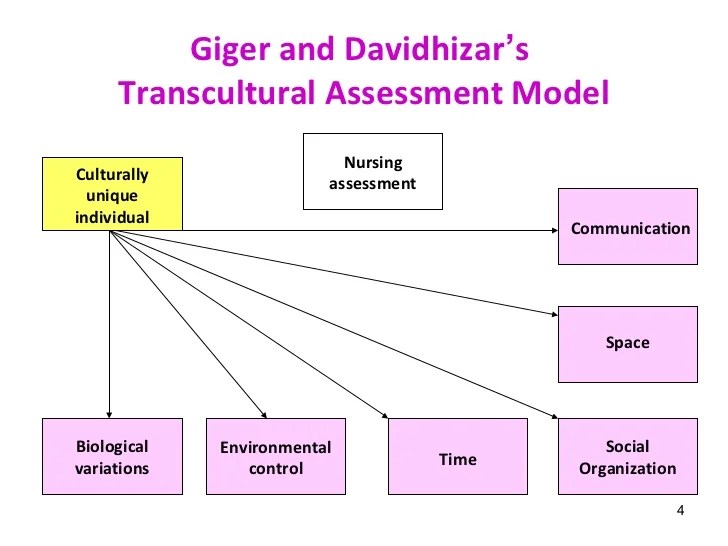
The GD TAM consists of six cultural assessment domains: communication, space, time, social organization, environmental control, and biological variations. These domains encompass a broad range of cultural factors that can influence health outcomes, such as language barriers, healthcare beliefs, and dietary practices.
By evaluating each domain, healthcare providers can gain a deeper understanding of their patients’ cultural backgrounds and develop tailored care plans that respect and accommodate their cultural needs.
1. Giger Davidhizar Transcultural Assessment Model
Overview
The Giger Davidhizar Transcultural Assessment Model (GD TAM) is a comprehensive framework designed to assess cultural diversity and its impact on healthcare interactions. Developed by Joyceen S. Giger and Mary Ann Davidhizar in 1988, the model provides a systematic approach to understanding cultural influences on health beliefs, values, and behaviors.
The GD TAM is grounded in the theory of cultural competence, which emphasizes the importance of healthcare providers being aware of and responsive to cultural differences in order to provide culturally sensitive care. The model has been widely adopted in healthcare settings and has been shown to improve patient-provider communication, reduce health disparities, and promote cultural competence.
2. Components of the GD TAM
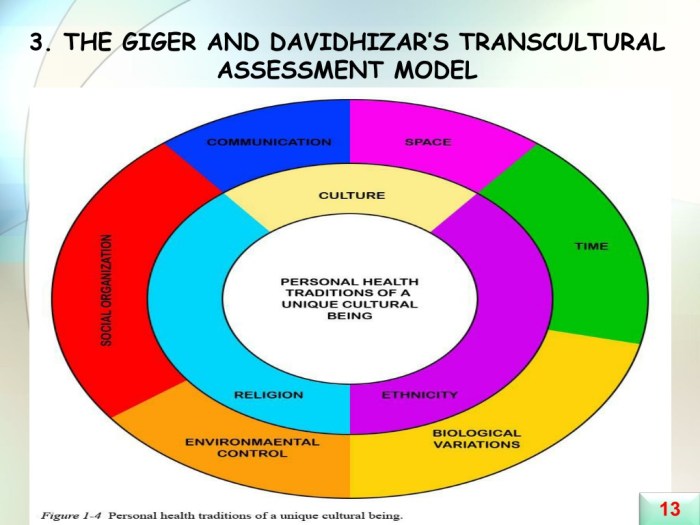
The GD TAM consists of six cultural assessment domains, each representing a key aspect of cultural diversity:
- Communication: Includes language, nonverbal communication, and communication patterns.
- Space: Refers to personal space, territoriality, and the use of physical space.
- Time: Encompasses perceptions of time, punctuality, and the organization of time.
- Environmental Control: Relates to beliefs about controlling the environment, health, and illness.
- Biological Variations: Includes genetic predispositions, nutritional practices, and health-related behaviors.
- Social Organization: Examines family structure, roles, and relationships, as well as social support systems.
Each domain is assessed using a variety of tools and methods, including observation, interviews, and questionnaires.
3. Applications of the GD TAM in Healthcare
The GD TAM has numerous applications in healthcare settings, including:
- Improving patient-provider communication: By understanding cultural differences in communication styles, healthcare providers can adapt their communication strategies to enhance patient comprehension and satisfaction.
- Reducing health disparities: The GD TAM helps identify cultural factors that may contribute to health disparities, enabling healthcare providers to develop targeted interventions to address these disparities.
- Promoting cultural competence: The model provides a framework for healthcare providers to develop cultural competence, which is essential for providing culturally sensitive and equitable care.
- Integrating into healthcare education: The GD TAM is widely used in healthcare education and training programs to prepare healthcare professionals to work effectively with diverse patient populations.
4. Strengths and Limitations of the GD TAM: Giger Davidhizar Transcultural Assessment Model
The GD TAM offers several strengths, including:
- Comprehensive: The model covers a wide range of cultural domains, providing a holistic understanding of cultural diversity.
- Systematic: The GD TAM provides a structured approach to cultural assessment, ensuring consistency and reliability.
- Evidence-based: The model is supported by extensive research and has been shown to improve patient outcomes.
However, the GD TAM also has some limitations:
- Time-consuming: The GD TAM can be time-consuming to administer, especially in busy healthcare settings.
- Complexity: The model is complex and requires training to use effectively.
- Cultural bias: The GD TAM may not be equally applicable to all cultures and may need to be adapted to specific cultural contexts.
5. Comparative Analysis of the GD TAM and Other Transcultural Assessment Models
Several other transcultural assessment models exist, each with its unique strengths and limitations. Some commonly used models include:
- Leininger’s Culture Care Diversity and Universality Theory: Focuses on the relationship between culture and nursing care, emphasizing the importance of understanding cultural values and beliefs.
- Purnell’s Model for Cultural Competence: Provides a framework for assessing cultural competence at the individual, organizational, and societal levels.
The GD TAM differs from these models in its comprehensive approach, which includes a wider range of cultural domains and provides specific guidance for assessing each domain.
6. Future Directions and Innovations in Transcultural Assessment
The field of transcultural assessment is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging:
- Technology and artificial intelligence: Advancements in technology are being used to develop new tools and methods for transcultural assessment, such as mobile apps and artificial intelligence-powered chatbots.
- Intercultural communication: Research is ongoing to explore the role of intercultural communication in transcultural assessment and how to effectively bridge cultural differences.
- Cultural humility: There is a growing emphasis on cultural humility in healthcare, which involves acknowledging one’s own cultural biases and limitations and seeking to learn from and collaborate with patients from diverse backgrounds.
These innovations are expected to enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of transcultural assessment in the future.
FAQ Compilation
What is the purpose of the GD TAM?
The GD TAM is designed to assess cultural diversity and its impact on healthcare interactions, helping healthcare professionals provide culturally sensitive and equitable care.
What are the six cultural assessment domains included in the GD TAM?
The GD TAM includes six domains: communication, space, time, social organization, environmental control, and biological variations.
How is the GD TAM used in healthcare?
The GD TAM is used to improve patient-provider communication, reduce health disparities, and promote cultural competence in healthcare settings.
What are the strengths of the GD TAM?
The GD TAM’s strengths include its comprehensive domains, systematic approach, and focus on cultural sensitivity.
What are the limitations of the GD TAM?
Potential limitations of the GD TAM include its reliance on self-reporting and the need for trained professionals to administer the assessment.