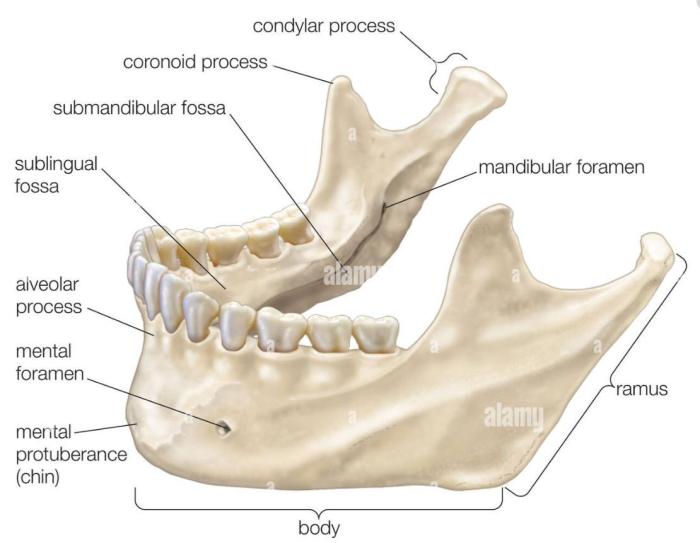
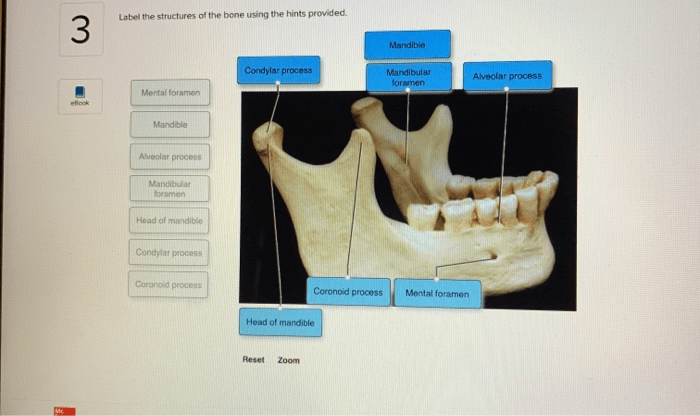
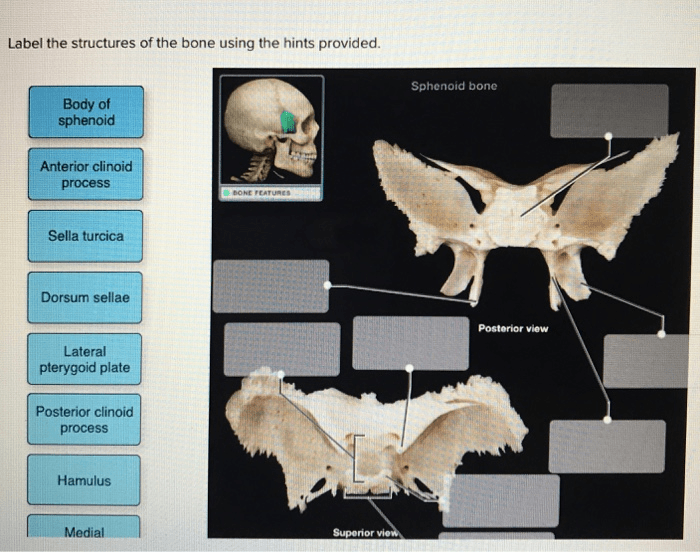
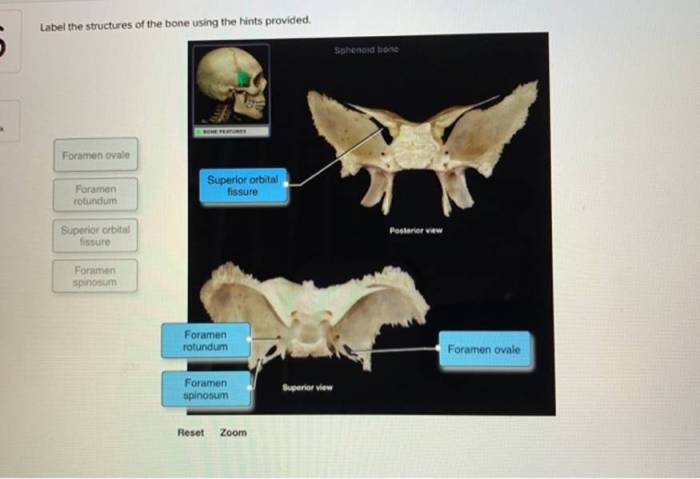
Label the structures of the bone using the hints provided. – Embarking on an exploration of bone anatomy, this comprehensive guide delves into the intricate structures that compose our skeletal framework. Label the structures of the bone using the hints provided, a captivating journey awaits, unveiling the secrets of bone composition, function, and development.
From the intricate arrangement of osteons in compact bone to the spongy network of trabeculae, we unravel the mysteries of bone’s remarkable strength and flexibility. Discover the vital role of bone cells, the composition of the bone matrix, and the dynamic processes of bone development and remodeling.
Bone Anatomy Overview: Label The Structures Of The Bone Using The Hints Provided.
Bones are the rigid components of the skeletal system that provide support, protection, and movement. They are composed of a hard outer layer called compact bone and a porous inner layer called spongy bone. The basic structure of a bone includes a shaft (diaphysis) and two ends (epiphyses), which are connected by a narrow region called the metaphysis.
Bones are composed of several types of cells, including osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. Osteoblasts are responsible for bone formation, while osteocytes maintain bone tissue and osteoclasts resorb bone tissue. The bone matrix is composed of collagen and hydroxyapatite, which give bone its strength and flexibility.
Compact Bone Structure
Compact bone is the dense outer layer of bone that provides strength and support. It is composed of osteons, which are cylindrical units of bone tissue. Each osteon contains a central Haversian canal, which carries blood vessels and nerves, and concentric lamellae of bone tissue.
Volkmann’s canals connect the Haversian canals and allow for the passage of blood vessels and nerves through the bone.
Spongy Bone Structure, Label the structures of the bone using the hints provided.
Spongy bone is the porous inner layer of bone that provides flexibility and shock absorption. It is composed of a network of thin, bony struts called trabeculae. The spaces between the trabeculae are filled with bone marrow, which produces blood cells.
Bone Cells
- Osteoblastsare cells that synthesize and secrete the organic matrix of bone.
- Osteocytesare mature bone cells that maintain bone tissue and regulate bone remodeling.
- Osteoclastsare cells that resorb bone tissue during bone remodeling.
Bone Matrix
The bone matrix is composed of collagen and hydroxyapatite. Collagen provides the bone with flexibility, while hydroxyapatite provides strength and hardness. The bone matrix is constantly being remodeled by osteoblasts and osteoclasts to maintain bone health.
Bone Development
Bone development begins in the embryo with the formation of cartilage models. These cartilage models are gradually replaced by bone tissue through a process called ossification. Bone growth continues throughout childhood and adolescence, and reaches its peak in early adulthood.
Bone Remodeling
Bone remodeling is a continuous process that involves the resorption of old bone tissue by osteoclasts and the formation of new bone tissue by osteoblasts. This process helps to maintain bone strength and flexibility, and to repair damaged bone.
Bone Diseases
- Osteoporosisis a condition in which bones become weak and brittle due to a loss of bone mass.
- Osteoarthritisis a degenerative joint disease that causes pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints.
- Bone canceris a type of cancer that affects the bones.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the different types of bone cells?
Osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts are the primary bone cell types, each playing distinct roles in bone formation, maintenance, and resorption.
What is the function of the bone matrix?
The bone matrix, composed of collagen and hydroxyapatite, provides structural support and flexibility to bones.
How does bone remodeling occur?
Bone remodeling is a continuous process involving bone resorption by osteoclasts and bone formation by osteoblasts, maintaining bone health and adapting to mechanical stress.