Review sheet exercise 7 the integumentary system – Review Sheet Exercise 7 delves into the fascinating realm of the integumentary system, the body’s protective barrier that plays a vital role in our overall well-being. This exploration unveils the intricate structure and functions of the skin, its accessory structures, common disorders, and essential tips for maintaining skin health.
The skin, the largest organ of the body, is a complex and dynamic organ that serves as a physical barrier, regulates body temperature, facilitates sensory perception, and contributes to immune defense.
Introduction

The integumentary system is the largest organ system in the human body. It consists of the skin, hair, nails, and glands. The integumentary system protects the body from the elements, helps regulate body temperature, and allows us to sense our surroundings.
Structure and Function of the Skin: Review Sheet Exercise 7 The Integumentary System
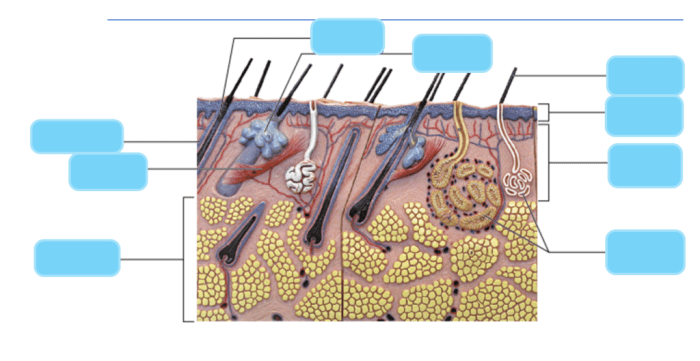
The skin is the largest organ of the integumentary system. It is made up of three layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin. It is made up of keratinized cells that protect the body from the elements.
Dermis
The dermis is the middle layer of the skin. It is made up of connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
Hypodermis
The hypodermis is the innermost layer of the skin. It is made up of fat cells that insulate the body and provide cushioning.
Functions of the Skin, Review sheet exercise 7 the integumentary system
- Protection: The skin protects the body from the elements, such as UV radiation, heat, and cold.
- Thermoregulation: The skin helps regulate body temperature by sweating and shivering.
- Sensation: The skin contains nerve endings that allow us to sense our surroundings.
- Excretion: The skin excretes waste products through sweat.
- Absorption: The skin can absorb certain substances, such as oxygen and vitamin D.
Accessory Structures of the Skin
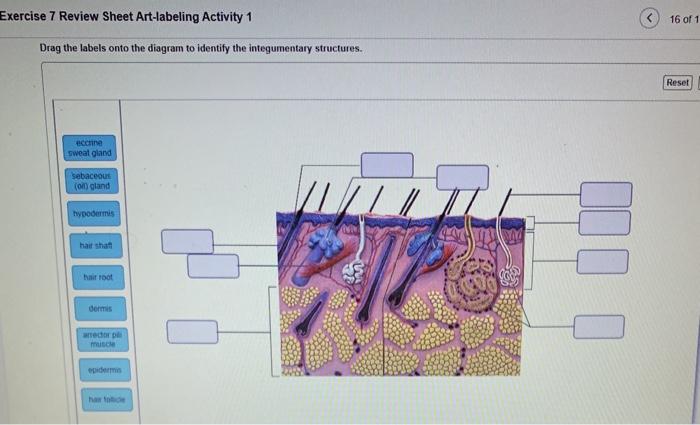
The accessory structures of the skin include hair, nails, and glands.
Hair
Hair is made up of keratinized cells. It helps to insulate the body and protect it from the elements.
Nails
Nails are made up of keratinized cells. They protect the tips of the fingers and toes.
Glands
There are two main types of glands in the skin: sweat glands and sebaceous glands.
- Sweat glands: Sweat glands produce sweat, which helps to regulate body temperature.
- Sebaceous glands: Sebaceous glands produce sebum, which helps to lubricate the skin.
Common Disorders of the Integumentary System
There are many common disorders of the integumentary system, including acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
Acne
Acne is a common skin disorder that is caused by the inflammation of the sebaceous glands.
Eczema
Eczema is a common skin disorder that is characterized by dry, itchy skin.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a common skin disorder that is characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin.
Maintaining Skin Health
There are many things you can do to maintain healthy skin, including:
- Protect your skin from the sun: The sun’s UV rays can damage the skin and lead to skin cancer. Wear sunscreen every day, even if it’s cloudy.
- Moisturize your skin: Moisturizing your skin helps to keep it soft and supple.
- Avoid harsh chemicals: Harsh chemicals can damage the skin. Avoid using harsh soaps and detergents.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to improve your skin’s health.
- Get regular exercise: Regular exercise can help to improve your skin’s circulation and appearance.
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the integumentary system?
The integumentary system primarily serves as a protective barrier against external threats, regulating body temperature, facilitating sensory perception, and contributing to immune defense.
What are the three layers of the skin?
The skin comprises three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis, each with unique functions and compositions.
What are some common skin disorders?
Common skin disorders include acne, eczema, and psoriasis, each characterized by distinct symptoms and underlying causes.