The cellular respiration flow chart answer key unveils the intricate dance of biochemical reactions that power life on Earth. This guide delves into the structure, steps, and energy yield of cellular respiration, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental process.
Cellular respiration is a complex series of chemical reactions that convert nutrients into energy, primarily in the form of ATP. This process occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. The cellular respiration flow chart answer key serves as a visual representation of these reactions, outlining the pathways and key intermediates involved.
Cellular Respiration Flow Chart Structure
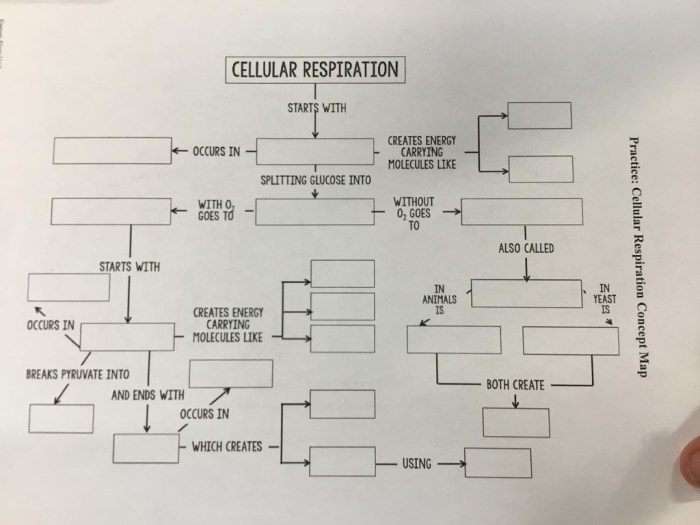
A cellular respiration flow chart is a visual representation of the steps involved in cellular respiration, the process by which cells convert glucose into energy. The flow chart is typically laid out in a linear fashion, with the reactants and products of each step listed in order.
The purpose of the flow chart is to provide a clear and concise overview of the cellular respiration process.
| Step | Reactants | Products |
|---|---|---|
| Glycolysis | Glucose | 2 Pyruvate |
| Pyruvate Oxidation | 2 Pyruvate | 2 Acetyl-CoA |
| Citric Acid Cycle | 2 Acetyl-CoA | 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 |
| Electron Transport Chain | 10 NADH, 2 FADH2 | 32-34 ATP |
Glycolysis: Cellular Respiration Flow Chart Answer Key
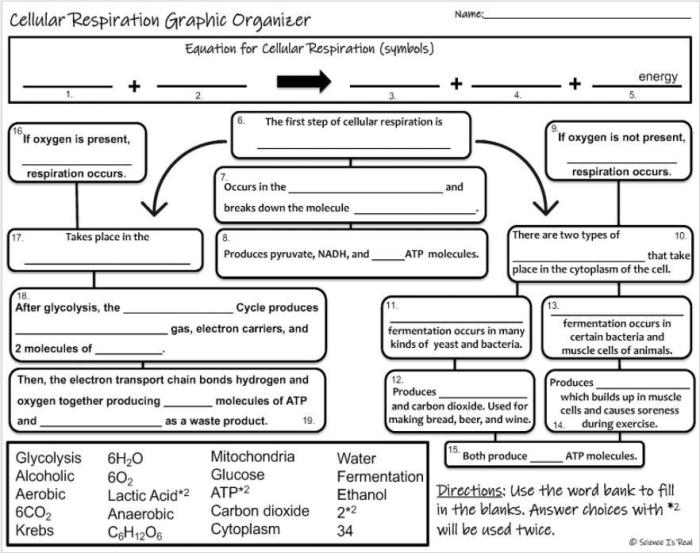
Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and does not require oxygen. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into two pyruvate molecules. The process is as follows:
- Glucose is phosphorylated to form glucose-6-phosphate.
- Glucose-6-phosphate is isomerized to fructose-6-phosphate.
- Fructose-6-phosphate is phosphorylated to form fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
- Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is cleaved into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
- Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is oxidized to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
- 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate is dephosphorylated to form 3-phosphoglycerate.
- 3-Phosphoglycerate is isomerized to 2-phosphoglycerate.
- 2-Phosphoglycerate is dehydrated to form phosphoenolpyruvate.
- Phosphoenolpyruvate is dephosphorylated to form pyruvate.
The energy yield of glycolysis is 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules.
Expert Answers
What is the purpose of glycolysis?
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and is responsible for breaking down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate.
What is the role of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
The electron transport chain is responsible for generating most of the ATP produced during cellular respiration through a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
How is cellular respiration regulated?
Cellular respiration is regulated by a variety of factors, including the availability of nutrients, oxygen, and hormones.